In today’s interconnected digital ecosystem, APIs are the critical connective tissue powering everything from mobile apps to complex enterprise systems and AI-driven platforms. A well-architected API is not just a technical asset; it’s a core business enabler that drives scalability, developer adoption, and innovation. Conversely, a poorly designed API can introduce security vulnerabilities, create performance bottlenecks, and accrue significant technical debt, hindering growth and exposing your organization to unnecessary risks.
This guide moves beyond theory to provide a comprehensive roundup of foundational api development best practices. We will deliver actionable strategies and real-world examples essential for building robust, secure, and future-proof digital products. For teams at SaaS companies, financial institutions, and enterprises, mastering these principles is the key to engineering reliable digital infrastructure that delivers tangible business value and a competitive edge.
You will learn how to:
- Implement robust security protocols like OAuth 2.0 and input validation to protect sensitive data.
- Design a clear and consistent API versioning strategy to manage change without breaking client integrations.
- Optimize performance through effective caching, payload management, and efficient data handling.
- Create comprehensive documentation that streamlines the developer experience and accelerates adoption.
By following these expert-level guidelines, your team can build APIs that serve as a solid foundation for your applications, supporting scalable growth, operational excellence, and long-term business success.
1. Master RESTful API Design Principles for Predictability and Scale
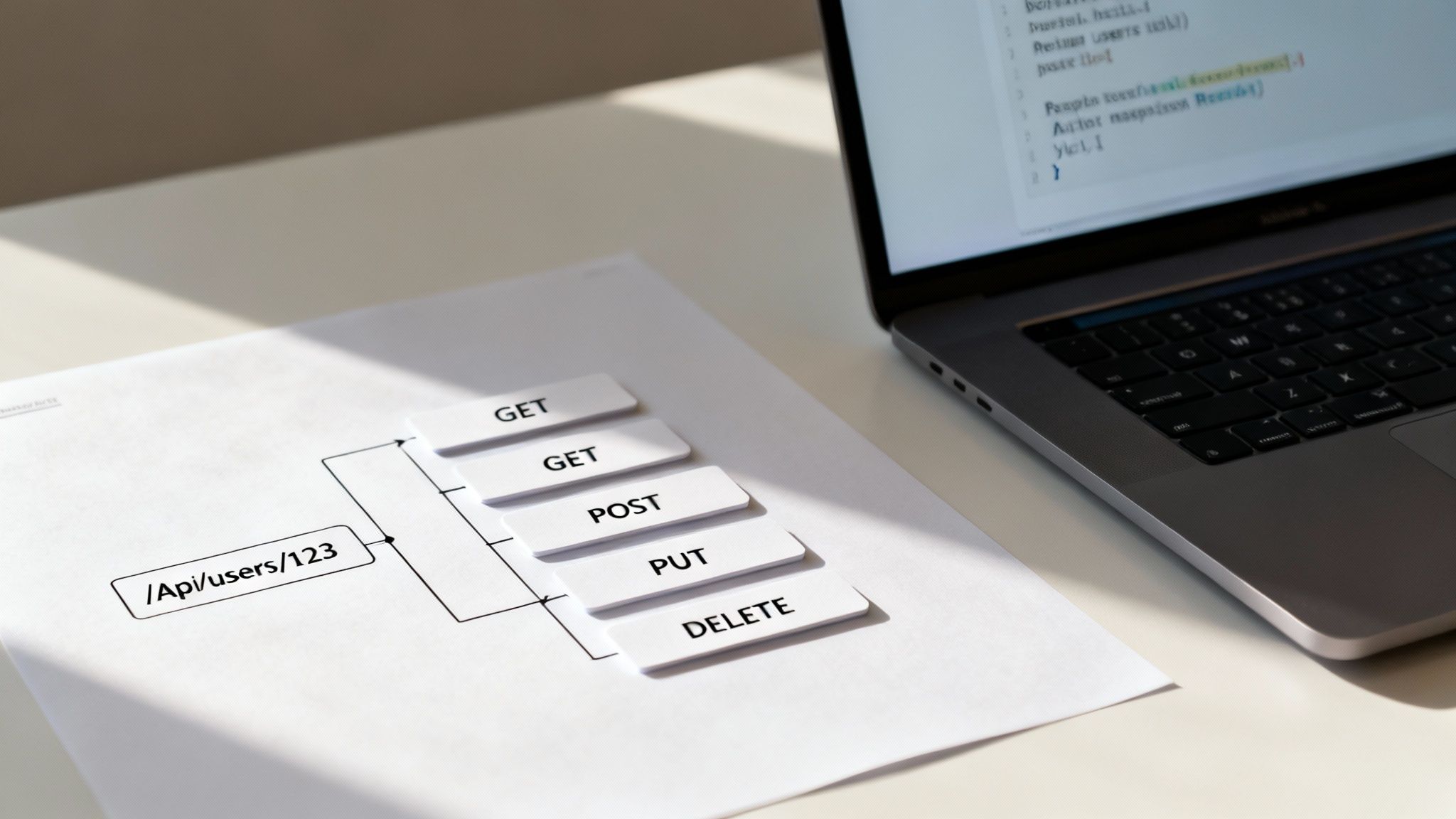
Adhering to REST (Representational State Transfer) principles is a cornerstone of modern API development best practices. This architectural style uses standard HTTP methods and logical, resource-based URLs to create a uniform interface that developers can easily understand and predict. By treating every business entity as a resource, REST establishes an intuitive and consistent contract between the client and server, which is crucial for building scalable web services.
This approach emphasizes statelessness, meaning each request from a client contains all the information needed to be processed by the server, without relying on server-side session state. This decoupling simplifies server design, enhances reliability, and is essential for horizontal scaling. For any SaaS, e-commerce, or fintech platform, a clean RESTful design is the foundation for a positive developer experience and a maintainable, high-performance system.
Why This Matters for Business
REST’s power lies in its simplicity and use of established web standards. Leading platforms like Stripe and GitHub exemplify this. Stripe’s API uses clear, resource-based endpoints like /v1/charges, while GitHub’s API allows interaction with repositories via intuitive endpoints such as /repos/{owner}/{repo}. This predictability minimizes the learning curve for developers, accelerating integration timelines and reducing costly errors, which directly translates to faster time-to-market for new features and products.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To apply these principles effectively, your development team should standardize on the following conventions:
- Use Plural Nouns for Collections: Always name resource collections with plural nouns for clarity (e.g.,
/api/v1/ordersinstead of/api/v1/order). This consistency improves readability and predictability. - Implement Proper HTTP Status Codes: Use standard HTTP methods and status codes to provide meaningful feedback. For instance, return
201 Createdfor a successfulPOSTrequest that creates a new resource, not just a generic200 OK. - Utilize Query Parameters for Operations: For filtering, sorting, and pagination, use query parameters. A request like
/api/v1/products?sort=price_desc&limit=25is self-explanatory, powerful, and keeps the base URL clean. - Manage Resource Relationships: Nesting can show relationships (e.g.,
/api/v1/customers/123/orders), but avoid deep nesting beyond one or two levels to prevent overly complex and rigid URLs that are hard to maintain.
2. Implement Comprehensive API Documentation for Seamless Adoption
An API is only as good as its documentation. Without clear, comprehensive guides, even the most powerful API will struggle with adoption and create a support burden. One of the most critical API development best practices is treating documentation as a first-class product, providing developers with everything they need to integrate successfully. This includes detailed endpoint descriptions, authentication methods, error codes, rate limits, and request/response examples.
This developer-centric approach transforms documentation from a mere reference into an essential tool for usability. For any platform, especially in SaaS or fintech where integrations are a key revenue driver, high-quality documentation directly correlates with faster adoption rates, fewer support tickets, and a stronger developer community, ultimately improving ROI.
Why This Matters for Business
Exceptional documentation removes friction and builds trust, which are key to fostering a successful developer ecosystem around your product. Leading platforms like Stripe and Twilio are renowned for their developer portals. Their interactive documentation allows developers to make live API calls directly from the browser, providing immediate feedback and accelerating the learning process. This hands-on experience is invaluable and significantly reduces the time-to-value for new users.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To create documentation that empowers developers and drives adoption, your team should prioritize the following practices:
- Use OpenAPI/Swagger Specifications: Standardize your API definition using the OpenAPI Specification. This allows you to auto-generate interactive documentation, client SDKs, and server stubs, ensuring your docs are always synchronized with your code.
- Include Real-World Code Examples: Provide copy-and-paste code snippets in multiple popular programming languages (e.g., Python, JavaScript, Java, Go). Showcase common business use cases to help developers get started quickly.
- Provide a Sandbox Environment: Offer a dedicated testing or sandbox environment where developers can experiment with the API without affecting production data. This is crucial for building and validating integrations safely and efficiently.
- Create Quick-Start Guides: Develop step-by-step tutorials for common tasks, such as “making your first call” or “processing a payment.” These guides simplify the onboarding journey and improve the overall developer experience.
3. Implement a Clear API Versioning Strategy
An effective API versioning strategy is a critical component of API development best practices, ensuring your API can evolve without breaking client integrations. As you add features, fix bugs, or refactor your codebase, changes are inevitable. Versioning provides a clear contract that allows you to introduce these changes, including breaking ones, while giving consumers a predictable and stable migration path.
This approach is fundamental to long-term API health and developer trust. By explicitly managing versions, you prevent sudden failures in client applications, which is essential for maintaining relationships with partners and customers. For any platform, especially in enterprise SaaS and fintech where stability is paramount, a well-defined versioning plan is non-negotiable for sustainable growth.
Why This Matters for Business
Versioning’s value lies in its ability to support backward compatibility while enabling innovation. Leading API-first companies like Stripe and Twitter demonstrate its importance. Stripe is famous for its long-term support of API versions, allowing users to upgrade on their own schedule, which builds immense trust. Twitter’s move from API v1.1 to v2 provided a completely new, more powerful interface while keeping the older version available for a transition period. This managed evolution builds confidence and encourages adoption.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To implement a robust versioning strategy, your team should adopt a consistent and well-communicated approach:
- Choose a Versioning Method: The most common and explicit method is URL versioning (e.g.,
/api/v2/users), as it’s easy to see in logs and browsers. Other options include custom request headers (Accept: application/vnd.myapi.v2+json) or query parameters. - Use Semantic Versioning (SemVer): Apply SemVer (MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH) principles. Increment the MAJOR version for breaking changes, MINOR for backward-compatible new features, and PATCH for backward-compatible bug fixes.
- Plan Deprecation Timelines: When introducing a new major version, clearly communicate the deprecation schedule for the old one. A minimum of 6 to 12 months is standard practice to give consumers adequate time to migrate their applications.
- Provide Migration Guides: For every major version release, publish a comprehensive migration guide. Document what has changed, why it changed, and provide clear code examples to facilitate a smooth transition for developers.
4. Implement Robust Error Handling and Meaningful Status Codes
Effective error handling is a critical, yet often overlooked, component of API development best practices. A robust strategy goes beyond simply catching exceptions; it provides clear, actionable feedback to API consumers, enabling them to diagnose and resolve issues efficiently. By using standard HTTP status codes and a consistent, detailed error response format, you create a predictable and developer-friendly interface that builds trust and accelerates integration.
This approach ensures that when something goes wrong, the client isn’t left guessing. A well-designed error response explains what happened, why it happened, and potentially how to fix it. For any application relying on your API, this clarity is the difference between a frustrating dead-end and a quick, self-service resolution, which directly reduces support costs and improves developer satisfaction.
Why This Matters for Business
The power of great error handling is evident in leading APIs like Stripe. When a request fails, Stripe returns a detailed JSON object containing a specific code (e.g., card_declined), a human-readable message, and other contextual data. This allows developers to programmatically handle different failure scenarios, such as prompting a user to provide a new payment method. Vague errors force developers into a cycle of trial-and-error debugging, wasting valuable time and delaying project timelines.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To build a reliable error handling system, your team should adopt a standardized approach:
- Use a Consistent Error Response Format: Standardize your error structure. A common format like
{"error": {"code": "invalid_api_key", "message": "The provided API key is not valid."}}makes parsing errors predictable and automation-friendly. - Implement Specific HTTP Status Codes: Don’t default to
400 Bad Requestfor all client-side errors. Use401 Unauthorizedfor authentication issues,403 Forbiddenfor authorization failures, and404 Not Foundfor missing resources. - Provide Actionable Error Messages: Instead of just saying “Invalid input,” tell the developer which field was incorrect and why (e.g., “The ’email’ field must be a valid email address.”).
- Never Expose Internal Stack Traces: Leaking internal system details like stack traces in production error responses is a significant security vulnerability. Log them server-side for debugging but provide a clean, safe response to the client.
5. Security: Implement Robust Authentication and Authorization
Securing an API is non-negotiable, as it directly protects sensitive data, prevents unauthorized access, and maintains business integrity. This critical layer of API development best practices is handled by two distinct processes: authentication (verifying a user’s identity) and authorization (defining what that verified user is allowed to do). A failure in either can lead to catastrophic data breaches, regulatory fines, and loss of customer trust.
Implementing a modern security model involves choosing the right strategy for your specific use case, whether it’s API keys for simple access, OAuth 2.0 for delegated user permissions, or JWTs for stateless sessions. For any platform handling user data—especially in fintech, e-commerce, or government sectors—a strong, multi-layered security approach is essential for building a resilient and trustworthy system.
Why This Matters for Business
Proper security protocols ensure that only legitimate clients can access your API and that they can only perform actions they are permitted to. This principle of least privilege is fundamental to risk management. For example, Google’s OAuth 2.0 implementation allows an application to request specific permissions (scopes), like “read-only access to Google Drive,” without ever exposing the user’s password to the third-party app. This granular control is vital for protecting user privacy and system integrity.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To build a secure API, your team must integrate security from the very beginning. For more in-depth strategies, explore these REST API security best practices.
- Enforce HTTPS/TLS: Always encrypt data in transit by using HTTPS across all API endpoints. Never transmit sensitive information over an unencrypted channel.
- Use Proven Frameworks: Implement standard protocols like OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect. Platforms like Auth0 or Okta can significantly reduce development time and security risks by handling the complexities of identity management.
- Implement Token Expiration: Use short-lived access tokens (e.g., JWTs) and implement a secure refresh token mechanism to limit the window of opportunity for attackers if a token is compromised.
- Define Granular Scopes: Use authorization scopes to grant clients the minimum level of access required to perform their functions. A read-only client should never have write permissions.
6. Implement Robust Rate Limiting and Throttling to Ensure Stability
Implementing rate limiting and throttling is a critical API development best practice for protecting your services from abuse and ensuring fair usage for all consumers. Rate limiting controls the number of API requests a user can make in a given time frame, preventing any single client from overwhelming the system. Throttling, a related concept, gracefully manages high traffic loads by slowing down responses when demand exceeds capacity, ensuring the API remains available and responsive.
These mechanisms are essential for maintaining API stability, security, and reliability. By preventing denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and ensuring equitable resource distribution, rate limiting and throttling safeguard your infrastructure and guarantee a consistent quality of service. For any scalable platform, from fintech applications to SaaS products, these controls are non-negotiable for sustainable operation and a positive developer experience.
Why This Matters for Business
Effective rate limiting protects your API’s backend resources, creates a predictable environment for consumers, and can even enable new business models (e.g., tiered pricing based on usage). The GitHub API, for instance, limits unauthenticated requests to 60 per hour but increases this to 5,000 for authenticated users, encouraging proper integration. Similarly, Stripe’s API enforces limits to ensure its financial infrastructure remains stable and responsive for all merchants. These policies are not just protective; they are a core part of the API product design.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To implement rate limiting effectively, your team should build clear policies and communicate them transparently:
- Communicate Limits via HTTP Headers: Always include headers in your API responses to inform clients of their current status. Common headers include
X-RateLimit-Limit(the total requests allowed),X-RateLimit-Remaining(requests left in the window), andX-RateLimit-Reset(the time when the limit resets). - Use the
429 Too Many RequestsStatus Code: When a client exceeds their limit, respond with a429status code. Crucially, include aRetry-Afterheader indicating how long the client should wait before making another request. - Encourage Exponential Backoff: Document and recommend that clients implement an exponential backoff strategy. This client-side pattern reduces request frequency after a failure, preventing a thundering herd of retries that could worsen server load.
- Monitor and Adjust Limits: Your initial limits may not be perfect. Continuously monitor API usage patterns to identify if limits are too restrictive for valid use cases or too permissive to prevent abuse, and adjust them accordingly.
7. Implement Rigorous Input Validation and Sanitization
Treating all incoming data as potentially malicious is a foundational API development best practice for security and stability. Input validation and sanitization act as your API’s first line of defense, ensuring that all data conforms to expected types, formats, and constraints before it is processed. This protects against a wide range of security vulnerabilities, including injection attacks (SQLi, XSS), and prevents data corruption that can cause system-wide failures.
This two-step process involves validation (rejecting bad data) and sanitization (cleaning up potentially harmful data). By enforcing strict data integrity rules at the entry point, you create a more resilient and secure system. This is non-negotiable for any application, especially in fintech or e-commerce where data accuracy and security are paramount.
Why This Matters for Business
Never trust client-side validation alone. A malicious actor can easily bypass browser-level checks and send harmful payloads directly to your API, leading to data breaches or service disruptions. Enforcing validation on the server is the only reliable way to maintain security. The OWASP foundation lists injection attacks as one of the top security risks, making server-side validation a fundamental requirement for mitigating this threat and protecting business assets.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To build a robust defense, your team must integrate these validation and sanitization practices:
- Always Validate Server-Side: Treat client-side validation as a UX enhancement, not a security measure. All validation logic must be duplicated and enforced on the server.
- Adopt a Whitelist Approach: Instead of trying to block known bad inputs (blacklisting), define and allow only known good inputs (whitelisting). This is a far more effective and secure strategy.
- Use Schema Validation: Leverage tools like JSON Schema or built-in framework validators (e.g., in FastAPI or NestJS) to strictly define the expected structure, data types, formats (e.g., email, UUID), and value ranges for all incoming data.
- Sanitize Output: To prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, always sanitize data before rendering it back to a user. This involves encoding characters like
<,>, and&to prevent them from being executed as malicious code in a browser. - Log All Validation Failures: Systematically log failed validation attempts. This data is invaluable for security monitoring, helping you identify and respond to potential attacks or system abuse.
8. Implement Rigorous API Testing and Quality Assurance
A reliable API is a non-negotiable component of modern software, and rigorous testing is the only way to guarantee it. Comprehensive API development best practices mandate a multi-layered testing strategy that validates functional correctness, performance under load, and security vulnerabilities. This process ensures that your API not only works as expected but is also robust, secure, and ready for production-level traffic.
Automated testing is the cornerstone of modern quality assurance (QA), enabling teams to run checks continuously and catch regressions before they impact users. By integrating test suites into the CI/CD pipeline, you establish a quality gate that maintains stability and accelerates development cycles. For any organization building a scalable product, investing in thorough testing is essential for delivering a dependable and trustworthy developer experience.
Why This Matters for Business
An untested or poorly tested API is a significant business risk, leading to data corruption, security breaches, and costly system downtime. By implementing a robust QA process, you build confidence in every deployment. For example, a fintech platform can use automated tests to verify that transaction endpoints correctly handle edge cases like invalid currency formats or insufficient funds, preventing financial errors. Similarly, an e-commerce API can use load testing to ensure it can handle a Black Friday traffic surge without crashing, protecting revenue.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To build a comprehensive and automated testing framework, your team should prioritize the following actions:
- Implement a Testing Pyramid: Employ a mix of unit tests (for individual components), integration tests (for service interactions), and contract tests (to ensure consumer-provider contracts are met).
- Test Error Paths and Edge Cases: Go beyond the “happy path.” A robust API gracefully handles invalid inputs, unauthorized requests, and unexpected server states. Test for correct error codes and messages.
- Use Realistic Test Data: Populate your testing environment with data that mirrors production scenarios. This helps uncover issues related to data volume, character sets, and complex relationships that simple mock data might miss.
- Integrate Testing into CI/CD: Automate your test suites to run on every commit or pull request. This provides immediate feedback to developers and prevents bugs from being merged into the main branch. You can learn more about software testing best practices to strengthen your process.
9. Prioritize API Performance Optimization and Caching for Speed and Efficiency
Optimizing API performance is a critical practice that directly impacts user experience, scalability, and operational costs. A fast, responsive API feels reliable to consumers, while sluggish performance can lead to user frustration, application abandonment, and lost revenue. Core strategies involve minimizing latency through efficient database queries, reducing payload sizes, and implementing intelligent caching mechanisms to serve frequent requests without repeatedly hitting backend systems.
This proactive approach is fundamental to building resilient and cost-effective services. By reducing the computational load on servers, optimization enhances an API’s ability to handle high traffic volumes and scale efficiently. For any platform where responsiveness is key, from e-commerce checkouts to real-time fintech data feeds, performance optimization is an essential part of the api development best practices lifecycle.
Why This Matters for Business
Slow APIs degrade the user experience and can become a significant financial drain through increased infrastructure costs. Netflix, for instance, heavily invests in API optimization to deliver seamless streaming to millions of users simultaneously. They employ sophisticated caching and data compression to reduce latency. Similarly, GitHub’s API uses HTTP caching headers like Cache-Control and ETag to allow clients and proxies to cache responses, significantly reducing the load on their servers and improving response times for developers.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To build a high-performance API, your team should integrate the following techniques into your development workflow:
- Implement HTTP Caching Headers: Use
Cache-Control,ETag, andLast-Modifiedheaders to enable client-side and intermediary caching (like CDNs). This is the first line of defense against unnecessary requests for static or semi-static data. - Use Pagination for Large Datasets: Never return an entire database table in one response. Implement pagination using limit/offset or cursor-based methods to break large result sets into manageable chunks.
- Compress API Responses: Enable gzip or Brotli compression on your web server or API gateway. This can dramatically reduce the size of JSON payloads, speeding up transfer times, especially on mobile networks.
- Leverage In-Memory Caching: Use tools like Redis or Memcached to cache frequently accessed, non-volatile data. This avoids expensive database queries for common information, such as user profiles or product catalogs, significantly improving response times.
10. Implement Comprehensive Monitoring, Logging, and Observability
Effective API development best practices extend far beyond the initial build; they require continuous insight into how your API behaves in a live environment. Monitoring, logging, and observability provide this critical visibility, allowing you to detect issues proactively, debug errors efficiently, and understand system performance under real-world load. This combination of metrics, logs, and traces is essential for maintaining reliability and a high-quality developer experience.
By capturing detailed data on requests, responses, and internal processes, you move from a reactive to a proactive operational model. This is especially crucial in microservices architectures where a single API call might traverse multiple services. Without a robust observability strategy, identifying the root cause of latency or an error becomes nearly impossible, impacting user trust and system stability.

Why This Matters for Business
Observability gives you the power to ask questions about your system that you didn’t know you needed to ask, which is key to maintaining service level agreements (SLAs). While monitoring tells you if something is wrong (e.g., high error rate), observability helps you understand why. Tools like Datadog, New Relic, or open-source solutions like the ELK Stack provide the platforms needed for this deep insight. This practice is integral to modern DevOps, closely tying into the feedback loops established by a well-structured CI/CD pipeline.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
To build a comprehensive observability framework, your team should focus on the following practical steps:
- Implement Structured Logging: Use a consistent format like JSON for logs. This makes them machine-readable, simplifying searching, filtering, and analysis in tools like Elasticsearch or Datadog.
- Include a Correlation ID: Generate a unique ID for every incoming request and pass it through all downstream services. This correlation ID is invaluable for tracing a single transaction across a distributed system.
- Log at Appropriate Levels: Use standard logging levels (DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR) to control verbosity. This allows you to filter logs effectively in different environments without code changes.
- Never Log Sensitive Data: Be vigilant about scrubbing Personally Identifiable Information (PII), API keys, passwords, and other sensitive data from your logs to maintain security and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Track the “four golden signals” of monitoring: latency, traffic, errors, and saturation. Set up automated alerts for when these metrics exceed predefined thresholds to enable rapid response.
From Principles to Production: Your Next Steps in API Excellence
We’ve explored ten foundational pillars of modern API development, moving from the architectural elegance of RESTful design to the non-negotiable demands of robust security and deep observability. Mastering these API development best practices is not about checking boxes; it’s about building a strategic foundation for your digital products. An API is no longer just a technical endpoint; it is the central nervous system of your application, the gateway for your partners, and the engine for your user experiences.
Treating your API as a first-class product is the core theme connecting all these practices. This means prioritizing the developer experience with crystal-clear documentation, implementing a predictable versioning strategy to prevent breaking changes, and providing meaningful, structured error messages. It means building trust through layers of security like robust authentication, authorization, and vigilant input validation. It also means guaranteeing reliability through performance optimization, intelligent caching, and comprehensive monitoring that tells you not just if something is broken, but why.
Adopting this mindset transforms your API from a simple utility into a powerful business asset that drives growth. It accelerates development for both internal and external teams, fosters innovation by making your services easily consumable, and builds a reputation for quality and reliability in a crowded digital marketplace. The difference between a functional API and an excellent API lies in the deliberate and consistent application of these principles.
Key Takeaways for Immediate Impact
To translate these concepts into tangible improvements, focus on these critical areas:
- Design and Documentation First: A well-designed, contract-first API with comprehensive, interactive documentation prevents misunderstandings, reduces integration friction, and serves as the single source of truth for all consumers.
- Security is Non-Negotiable: A single vulnerability can compromise your entire system. Layer your defenses with strong authentication (OAuth 2.0), precise authorization, rate limiting, and rigorous input validation. Security cannot be an afterthought.
- Observability Over Monitoring: Don’t just collect logs and metrics. Implement structured logging, distributed tracing, and real-time monitoring to gain deep, actionable insights into your API’s health, performance, and usage patterns. This is essential for proactive maintenance and scaling.
- Automation is Your Ally: Automate everything you can, especially testing. Integrating comprehensive test suites (unit, integration, contract, and end-to-end) into your CI/CD pipeline is the single most effective way to ensure consistent quality, reliability, and developer velocity.
Your Actionable Next Steps
Embarking on this journey of API excellence requires a structured approach. Don’t attempt to overhaul everything at once. Instead, build momentum with targeted, high-impact changes.
- Conduct an API Audit: Select one of your most critical API endpoints. Using the ten best practices from this article as a checklist, perform a candid audit. Where are the most significant gaps? Is documentation outdated? Is error handling inconsistent? Are security headers missing?
- Prioritize One High-Value Improvement: Choose the single improvement that will deliver the most business value or mitigate the most risk. For a public-facing API, this might be implementing rate limiting. For an internal API, it could be improving your structured logging to simplify debugging.
- Establish an API Governance Framework: Create a lightweight set of internal standards and guidelines based on these best practices. This ensures that all new endpoints are built with quality, security, and consistency from day one, preventing technical debt from accumulating.
Building and maintaining world-class APIs requires a disciplined engineering culture and deep expertise. If your team needs to accelerate its product roadmap or scale its development capabilities with a partner who lives these principles daily, Group 107 can help. Our expert offshore engineering teams specialize in architecting and building secure, high-performance, and scalable digital solutions that drive tangible business outcomes. Contact Group 107 to learn how we can elevate your API strategy.




