In modern software delivery, DevOps automation is the engine that drives speed and reliability. It transforms a manual, error-prone workshop into a high-speed, automated assembly line for your code. The core objective is to replace slow, manual handoffs between development and operations teams with intelligent, automated workflows. This shift frees up your teams to focus on innovation while boosting velocity, system stability, and overall efficiency.
Understanding DevOps Automation
At its heart, DevOps automation uses strategic tools and processes to eliminate manual labor from the software development lifecycle (SDLC). If DevOps is the philosophy of collaboration and shared responsibility, automation is the practical framework that makes it achievable at scale.
Traditionally, developers would write code and "throw it over the wall" to the operations team for deployment. This siloed model created significant bottlenecks, communication breakdowns, and release cycles that were both painfully slow and inherently risky.
DevOps automation dismantles these silos, establishing a connected, repeatable, and transparent workflow that fosters trust and accountability across teams.
The Shift from Manual to Automated Processes
The contrast between manual and automated workflows is stark. Manual processes are slow, inconsistent, and a primary source of human error. A single misconfiguration on a server can lead to hours of downtime and significant revenue loss.
With an automated pipeline, every step—from code compilation to testing and production deployment—is executed identically every time. This guarantees consistency and predictability.
This transition is driven by a critical business need for agility and market responsiveness. Companies that master DevOps automation gain a significant competitive advantage:
- Accelerated Feature Release: Deploy updates in minutes or hours instead of weeks or months, allowing you to outpace competitors and respond to market demands in real time.
- Enhanced System Reliability: Automation minimizes manual errors, leading to more stable applications, improved user experience, and stronger customer trust.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, you empower your most skilled engineers to focus on high-value initiatives that drive business growth and innovation.
The momentum is undeniable. The global DevOps market is projected to reach USD 14,969.6 million by 2026, growing at a 19.1% compound annual growth rate. This highlights a clear industry-wide shift away from siloed teams and manual processes.
By embracing automation, businesses secure a critical advantage. To understand the foundational concepts, explore our guide on the basic tenets of DevOps services. Automation is no longer a luxury—it's essential for continuous innovation.
The Core Components of DevOps Automation
To truly understand what DevOps automation is, it's crucial to break it down into its core components. These are not isolated practices but interconnected pillars that support a powerful, resilient, and efficient software delivery engine. Together, they create a seamless pipeline that moves code from a developer's machine to a live production environment with speed and reliability.
Each component addresses a specific stage of the SDLC, replacing manual bottlenecks with automated precision. Let's examine these pillars to see how they function and why they are vital for any modern business.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD) are the twin engines of the DevOps pipeline. They are the heartbeat of automation, ensuring code flows smoothly and safely from development to production.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Developers frequently merge code changes into a central repository. Each merge automatically triggers a build and a suite of automated tests. The primary goal is to detect and resolve integration issues early, preventing them from escalating into major problems.
- Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD): Continuous Delivery ensures that any code change passing all automated tests is automatically deployed to a staging environment. Continuous Deployment takes it a step further by automatically releasing every validated change directly to production users.
For a SaaS company, a robust CI/CD pipeline is a strategic asset. It enables multiple daily deployments of new features and bug fixes with zero downtime, facilitating a rapid response to customer feedback. This immediate feedback loop provides a significant competitive edge. Learn more in our detailed article on what a CI/CD pipeline is.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) treats infrastructure provisioning and management—servers, networks, databases—as software development. Instead of manual configuration through GUIs, you define your entire infrastructure in version-controlled, human-readable code files.
This approach ensures consistency and repeatability. Tools like Terraform and Ansible interpret these files to automatically build and configure environments, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
With IaC, you can instantly provision identical development, testing, and production environments. This eliminates the "it worked on my machine" problem and prevents configuration drift between stages.
A fintech firm, for example, can use IaC to create perfectly replicated, compliant environments for testing and validation. During an audit, they can instantly demonstrate that their production infrastructure matches the approved, version-controlled code, simplifying regulatory compliance.
Configuration Management and Automated Testing
While IaC handles initial provisioning, Configuration Management ensures that infrastructure remains in its desired state throughout its lifecycle. It automates tasks like software installation, patch management, and policy enforcement across all servers, maintaining system-wide consistency.
Automated Testing serves as the quality gate for the entire pipeline. It involves executing a comprehensive suite of tests—unit, integration, end-to-end—at various stages to validate functionality and prevent regressions. Without robust automated testing, CI/CD would risk automating the deployment of defective code.
These practices are becoming standard. The DevOps market is projected to hit USD 18.44 billion by 2026 as more organizations leverage automation. Furthermore, businesses with mature DevOps practices invest 33% more in their infrastructure, enabling teams to focus on creating value rather than fighting fires.
The Tangible Business Impact of DevOps Automation
Implementing DevOps automation is a strategic business decision that delivers a clear and measurable return on investment (ROI). While the immediate benefit is faster code deployment, the real impact extends to the bottom line by fundamentally changing how you create and deliver value.
This transformation from technical efficiency to business outcomes drives revenue growth, reduces operational costs, and sharpens your competitive advantage. Instead of being constrained by quarterly release cycles, teams can deploy new features weekly or even daily, providing unmatched agility in any industry.
Accelerating Time-to-Market
The most immediate benefit of a well-implemented DevOps pipeline is the dramatic reduction in the time it takes to move an idea from concept to customer. By automating builds, testing, and deployments, you eliminate the bottlenecks that previously slowed down the entire process.
For an e-commerce platform, this means launching a holiday promotion in hours, not weeks, capturing timely market opportunities. For a SaaS provider, it means shipping a highly requested feature before a competitor can react.
Faster time-to-market is about more than speed—it's about market leadership. When you can innovate and deploy faster than your rivals, you set the industry pace and can respond to customer needs before they become a reason for churn.
Improving Product Quality and Reliability
Manual processes are inherently prone to human error. A single misconfiguration during a deployment can cause system-wide outages, eroding customer trust and incurring significant remediation costs. What is DevOps automation solving here? It enforces rigorous consistency, ensuring every deployment follows the same validated, error-free process.
Automated testing is the cornerstone of this reliability. By catching bugs early in the development cycle, you prevent them from ever reaching production. This proactive approach delivers key business benefits:
- Lower Remediation Costs: Fixing a bug in development is exponentially cheaper than fixing it post-release.
- Enhanced Customer Trust: Reliable applications build brand loyalty and protect your reputation.
- Reduced Downtime: Stable systems mean greater uptime, ensuring your services are consistently available to generate revenue.
Boosting Operational Efficiency and Team Morale
Automation liberates your most valuable assets—your engineers—from repetitive, low-impact tasks. Instead of manually managing servers or overseeing deployments, they can focus their expertise on innovation, complex problem-solving, and building features that directly contribute to business success.
This not only streamlines operations but also significantly boosts team morale and talent retention. High-performing engineers want to solve meaningful challenges, not perform manual toil.
Investing in a DevOps automation strategy is about building a more resilient, agile, and profitable organization. Discover how Group107 can help you implement your strategy with our specialized DevOps as a Service offerings.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Automation Toolkit
A successful DevOps automation strategy relies on a well-integrated toolchain. However, the sheer number of available tools can be overwhelming. The key is not to chase the latest trend but to select tools that address specific needs within your software delivery lifecycle.
Organizing your toolkit by functional categories is the most effective approach. This helps you build a cohesive technology stack that aligns with your business objectives, team skills, and budget. The goal is a seamless, automated workflow, not a disparate collection of software licenses.
Key Categories in the DevOps Toolchain
Instead of viewing tools in isolation, it's more effective to group them by the problems they solve. Each category represents a critical link in your automation pipeline, and the tools within them must integrate to ensure a smooth process.
Here are the essential tool categories to consider:
- Continuous Integration/Delivery (CI/CD): These tools are the core of your automation engine. Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI automate the building, testing, and deployment of code whenever a change is committed.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): These tools enable you to manage infrastructure programmatically. Terraform is the industry standard for provisioning cloud-agnostic resources, while Ansible excels at configuration management and application deployment.
- Containerization & Orchestration: Docker packages applications and their dependencies into portable containers, ensuring they run consistently across all environments. Kubernetes then automates the deployment, scaling, and management of these containerized applications at scale.
- Monitoring & Observability: You cannot manage what you cannot measure. Tools like Prometheus (for metrics collection), Grafana (for data visualization), and the ELK Stack (for logging) provide the real-time insights needed to maintain system health and performance.
The market for DevOps automation tools is expected to reach $14.44 billion by 2026, driven by the need to deliver software faster and more reliably. Tools like Ansible, Jenkins, and Docker are now standard for modern engineering teams.
Selecting the right combination requires strategic thinking. A startup might prefer the integrated platform of GitLab, while a large enterprise with a multi-cloud strategy may combine Terraform and Ansible for granular control. To explore your options further, read our in-depth DevOps tools comparison guide. The optimal toolkit is one that directly supports your business goals and transforms your automation strategy into a competitive advantage.
A Practical Roadmap to Implementing DevOps Automation
Transitioning to DevOps automation is a phased journey, not an overnight switch. A gradual, iterative approach minimizes risk, builds momentum, and demonstrates value at each stage. This practical roadmap guides you through a structured implementation that ensures team buy-in and delivers tangible wins along the way.
The first step is always to establish a clear baseline. Before you write a single line of automation script, you must thoroughly understand your current software delivery process.
Phase 1: Assess and Identify Bottlenecks
Begin by mapping every step your code takes from a developer's commit to production deployment. Involve stakeholders from development, operations, QA, and security to get a complete picture. The objective is to identify the most significant sources of friction and delay.
- Map the Value Stream: Visualize the entire workflow on a whiteboard to see where work slows down or gets stuck in manual handoffs.
- Identify Manual Toil: Pinpoint where your engineers are spending time on repetitive, low-value tasks like manual testing, server configuration, or deployments.
- Establish Baselines: Collect key metrics: What is your current lead time for changes? What is your deployment frequency? What is your change failure rate? These numbers are essential for demonstrating ROI later.
This initial assessment will highlight the most impactful areas for automation. For a SaaS company, the primary bottleneck might be a multi-day manual QA cycle. For an e-commerce business, it could be a high-risk, all-hands deployment process.
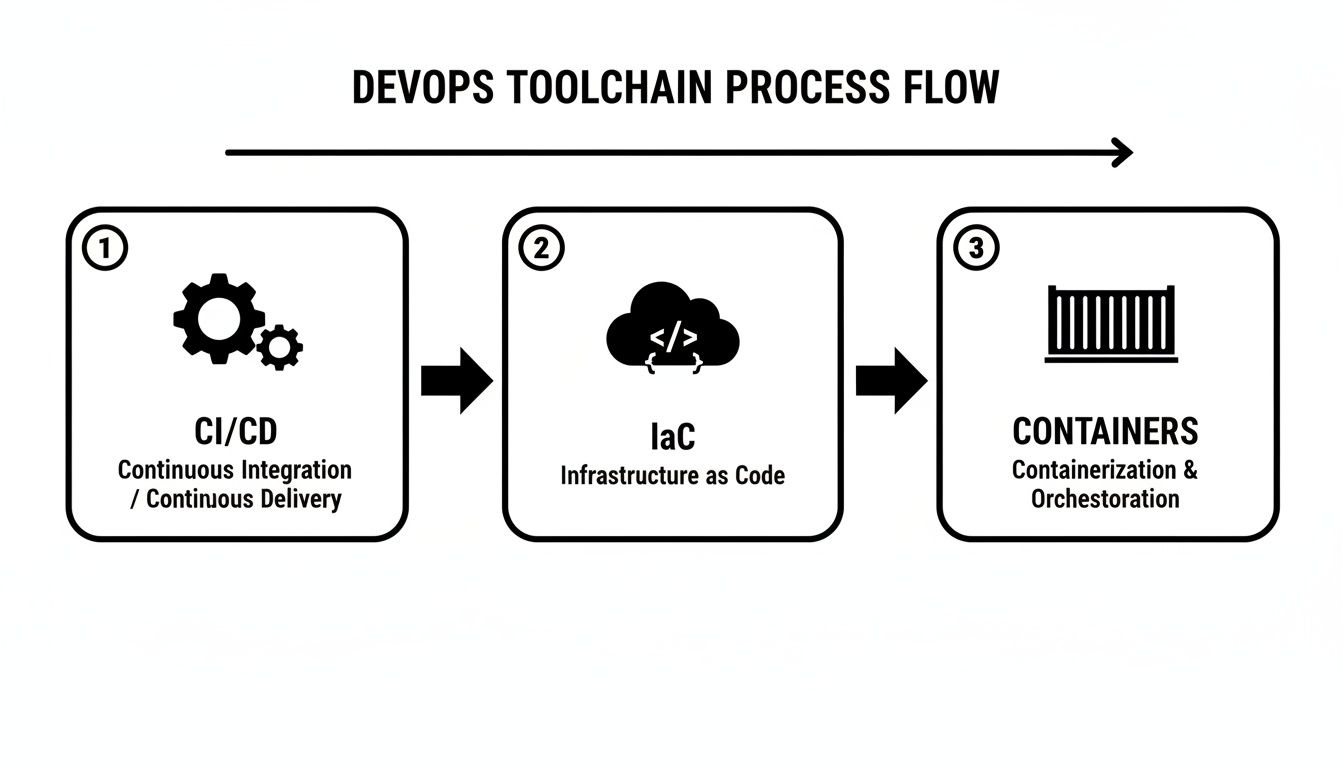
This flow illustrates how core DevOps automation components—CI/CD, Infrastructure as Code, and Containerization—integrate to create a continuous delivery pipeline.
The diagram clarifies that a successful pipeline is not about a single tool but the seamless integration of key practices to move code from developer to customer efficiently.
Phase 2: Launch a Pilot Project
After identifying a key bottleneck, resist the temptation to automate everything at once. Select a single, low-risk but high-visibility application for a pilot project. This creates a safe environment to experiment, learn, and demonstrate the benefits of automation without jeopardizing critical business operations.
Choose an internal application or a single microservice—something manageable in scope. The goal is to build your first functional CI/CD pipeline for this project.
A successful pilot is your most effective tool for driving cultural change. When other teams see the pilot team deploying code in minutes instead of days, they will be eager to adopt the new process.
Phase 3: Build, Secure, and Scale
With a successful pilot complete, it's time to scale. Use the lessons learned to create a reusable template or a "golden path" for other teams to follow. This is also the ideal time to integrate security into your automated workflows, a practice known as DevSecOps.
Your scaling strategy should include these key steps:
- Standardize Your Toolchain: Select a core set of tools for CI/CD, IaC, and monitoring to ensure consistency across the organization.
- Integrate Security Scans: Embed automated security testing (e.g., SAST, DAST) directly into the CI pipeline to identify vulnerabilities early.
- Develop an Internal Knowledge Base: Document best practices and provide training to empower other teams to adopt the automated workflow.
From here, you can incrementally onboard more applications and teams. By scaling methodically, you build a resilient, secure, and efficient delivery engine that supports business growth.
Ready to Make DevOps a Reality? Let's Talk.
Implementing a robust DevOps automation strategy can be a complex undertaking, particularly when facing internal skill gaps or resource constraints. This is where Group107 provides strategic value. We partner with you to translate the concepts discussed in this guide into tangible business outcomes.
Our DevOps as a Service model provides direct access to a dedicated team of elite engineers. We go beyond consultation to design, build, and manage your entire automation pipeline. This allows you to bypass the costly and time-consuming process of hiring specialized talent, providing a direct path to achieving your goals with potential cost savings of up to 60%.
From Theory to Execution
Knowing what DevOps automation is is one thing; making it work for your business is another. We bridge that gap with a focus on practical application and measurable results.
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: We build efficient CI/CD pipelines that move your products from idea to customer faster.
- Integrated Security and Compliance: We embed security into every stage of the lifecycle, ensuring your automated workflows are resilient and compliant from the start.
- Scalable and Resilient Operations: We design infrastructure that not only scales with your business but is also architected for high availability and rapid recovery.
Partnering with Group107 means gaining a dedicated engineering team fully invested in turning DevOps automation into your next competitive advantage.
Common Questions About DevOps Automation
As organizations explore what DevOps automation can achieve, several key questions consistently arise. Clear answers are essential for building a strategy that delivers real-world results. Let's address some of the most common inquiries.
What is the difference between DevOps and DevOps automation?
DevOps is the cultural philosophy that guides how development and operations teams collaborate. It emphasizes shared ownership, rapid feedback loops, and breaking down organizational silos to build and deliver software more effectively as a unified team.
DevOps automation is the technical implementation of that philosophy. It uses tools and practices like CI/CD pipelines, Infrastructure as Code, and automated testing to make the core DevOps principles of speed, reliability, and collaboration a reality. While a DevOps culture can exist without automation, its full potential can only be realized through it.
How do you measure the ROI of DevOps automation?
The most effective way to measure the ROI of DevOps automation is by tracking the four key DORA metrics. These provide a data-driven view of your software delivery performance.
- Deployment Frequency: How often do you successfully release code to production? Higher frequency indicates greater agility.
- Lead Time for Changes: How long does it take from a code commit to that change running in production? A shorter lead time means faster value delivery.
- Change Failure Rate: What percentage of your deployments results in a failure or requires remediation? A lower rate signifies higher quality and stability.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): When an incident occurs, how quickly can you restore service? A low MTTR demonstrates system resilience.
Tracking these metrics provides clear, quantifiable proof of the value generated by your automation investment.
Can small businesses benefit from DevOps automation?
Absolutely. DevOps automation is a powerful equalizer, enabling smaller teams to operate with the speed and reliability of much larger enterprises.
For startups and SMBs, it facilitates rapid product iteration, allows for confident feature releases, and enables on-demand infrastructure scaling—all without requiring a large, dedicated operations team. By automating the heavy lifting, it frees your team to focus on its core mission: building an exceptional product.
Summary and Next Steps
DevOps automation is the engine that translates the collaborative DevOps philosophy into tangible business results: faster time-to-market, improved product quality, and greater operational efficiency. By implementing core components like CI/CD, Infrastructure as Code, and automated testing, organizations can build a resilient and agile software delivery process.
Your Action Plan:
- Assess Your Current State: Map your software delivery value stream to identify the most significant manual bottlenecks.
- Start with a Pilot: Select a low-risk project to build your first CI/CD pipeline and demonstrate early wins.
- Scale Intelligently: Use your pilot's success to create standardized, secure, and reusable automation patterns across your organization.
Ready to transform your development lifecycle with expert-led automation? Group107 provides DevOps as a Service to help you build, secure, and scale your operations efficiently. Get in touch with us today.