User experience (UX) design is the strategic process of creating products that are effective, efficient, and enjoyable to use. It’s not about superficial aesthetics; it’s about engineering intuitive digital experiences that solve real user problems. Great UX design transforms complex operations into seamless, valuable journeys that build customer loyalty, drive conversions, and deliver measurable business growth.
What Is User Experience Design in a Business Context
User experience (UX) design is the architectural blueprint guiding every interaction a customer has with your product. It’s the behind-the-scenes discipline of making technology feel logical, valuable, and fundamentally human. While often confused with User Interface (UI) design, they serve distinct but complementary roles.
Here’s a clear analogy: if your application were a house, UI would be the paint color, furniture style, and visual finishes. UX, however, is the architectural plan—the logical flow between rooms, the placement of light switches, and the overall layout that makes the house functional and livable. UI is how it looks; UX is how it works.
Why UX Design Is a Business Imperative
In a competitive market, a clunky or confusing digital experience is the fastest way to lose a customer. Effective UX is not a "nice-to-have" feature; it is a core driver of business performance that directly impacts your bottom line.
Investing in strategic UX design delivers a powerful return on investment:
- Increased Conversion Rates: A streamlined checkout process on an e-commerce platform or a frictionless onboarding for a SaaS application removes friction, making it significantly more likely for users to complete key actions.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: When a product intuitively solves a problem, it builds trust and satisfaction. This turns first-time users into dedicated advocates who drive recurring revenue.
- Reduced Development Costs: Identifying and validating user needs through UX research and prototyping before development begins saves a fortune in costly rework and feature redesigns down the line.
For businesses in high-stakes industries like fintech, enterprise software, and e-commerce, UX isn’t just an advantage—it is the critical factor that determines product adoption, operational efficiency, and long-term profitability.
The Clear Distinction Between UX and UI
To build a successful digital product, understanding the difference between UX and UI is non-negotiable. They are deeply intertwined and both are essential, but they address different aspects of the design and development process.
This table provides a concise breakdown.
UX vs UI: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | User Experience (UX) Design | User Interface (UI) Design |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | The overall journey, logic, and effectiveness of the experience. | The visual presentation and interactive elements. |
| Core Question | "Does this solve the user's problem efficiently and logically?" | "Is this visually appealing and easy to interact with?" |
| Key Activities | User research, journey mapping, information architecture, wireframing. | Visual design, color theory, typography, component styling. |
| Goal | To create a product that is useful, usable, and accessible. | To create an interface that is aesthetically pleasing and intuitive. |
User Experience (UX) Design is the strategic foundation. UX designers focus on the why and the how. They conduct user research, map out information architecture, and create wireframes to ensure the entire product flow is logical and solves a real-world problem effectively.
User Interface (UI) Design is the tactical execution of the visual layer. UI designers handle the what and the look. They create style guides, design interactive components like buttons and forms, select typography and color palettes, and build the pixel-perfect mockups that users see and interact with.
Ultimately, a beautiful interface (UI) cannot salvage a product that is confusing or frustrating to use (UX). Both disciplines must collaborate seamlessly to create a solution that not only looks professional but functions flawlessly. Learn more about how we integrate these disciplines in our end-to-end design process.
The Core Principles of Effective UX Design
Exceptional user experience is not accidental; it is engineered upon a set of core principles that transform a functional product into an indispensable business asset. These pillars provide a strategic framework to ensure every design decision is intentional and user-centric.
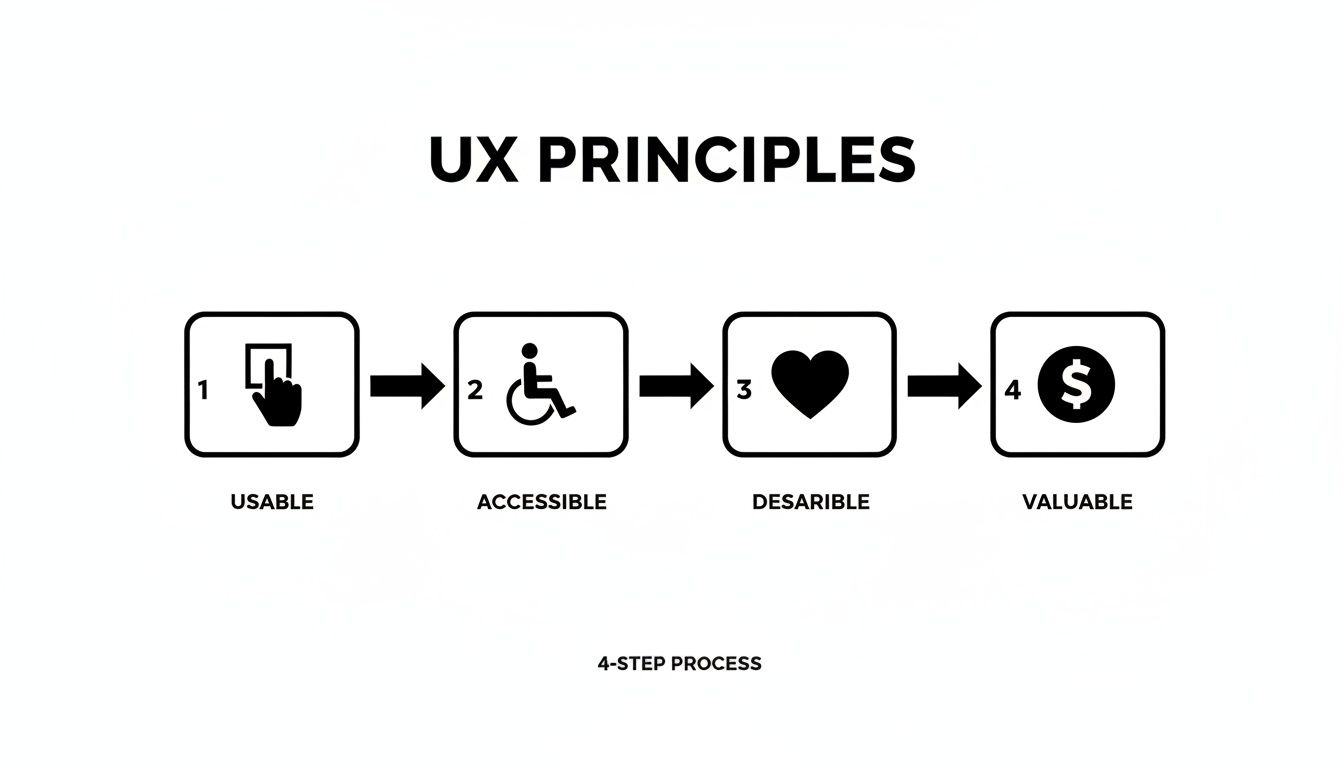
1. Usable
The foundational principle is usability. It answers a simple question: can a user accomplish their goal with ease and efficiency? If your fintech application requires five confusing steps to check an account balance, it fails the usability test. A usable product feels intuitive. Users shouldn't have to pause to figure out the next step; the path forward should be obvious. For a SaaS platform, this means a dashboard that surfaces the most critical tools and data upfront, saving users time and eliminating frustration.
2. Accessible
A product is not truly usable if it is not usable by everyone. Accessibility ensures that people with disabilities—including visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments—can use your product without barriers. This is not just a matter of compliance; it is a strategic business decision that expands your market reach. Adhering to standards like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) involves practical steps like adding alt text to images, ensuring sufficient color contrast, and enabling full keyboard navigation. Building an inclusive product requires a commitment to web accessibility best practices.
3. Desirable
Beyond pure functionality, a product must be desirable. This principle addresses the emotional connection a user forms with your solution. It's the difference between a tool people are forced to use and one they choose to use. Desirability is achieved through a thoughtful combination of branding, aesthetics, and interaction design that creates a positive, engaging experience. A sleek, modern investment app, for example, can make managing finances feel empowering rather than overwhelming, fostering brand loyalty.
4. Valuable
Finally, a product must deliver tangible value. It must solve a real-world problem or fulfill a genuine need more effectively than any alternative. Without delivering clear value, even the most beautiful and usable product will ultimately fail. Value is the core reason a user chooses your solution.
- For a B2B SaaS tool, value could be an automation feature that reduces manual data entry by 80%, boosting operational efficiency.
- For a fintech platform, value might be lower transaction fees or powerful analytics that enable better financial decision-making.
A product that integrates all four principles—usability, accessibility, desirability, and value—creates an undeniable competitive advantage and a foundation for sustainable growth.
The UX Design Process: From Discovery to Delivery
Great UX is the result of a structured, iterative process designed to mitigate risk and ensure the final product solves the right problem for the right users. This journey transforms an initial concept into a fully tested, user-validated solution.
By moving through distinct phases—discovery, strategy, design, and testing—teams can challenge assumptions early, avoiding the costly detours that result from building based on guesswork.
Stage 1: Research and Discovery
Every successful project begins with a deep dive into the problem space. The discovery phase is about replacing assumptions with data, developing genuine empathy for the user, and gaining a clear understanding of the business and market context.
Key activities in this stage include:
- User Interviews: Direct conversations with target users to uncover their motivations, pain points, and existing workflows.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Quantitative data collection to identify broad trends and validate qualitative findings.
- Competitive Analysis: Evaluating competitor products to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for differentiation.
A critical output of this stage is often a detailed visualization of the user's current process. A technique like customer experience journey mapping is invaluable for pinpointing specific pain points and opportunities for improvement.
The infographic below illustrates the core principles that guide the entire UX process, from initial research to final delivery.
This highlights how usability, accessibility, desirability, and value are interconnected pillars of a successful product strategy.
Stage 2: Strategy and Architecture
With a clear understanding of the "why" from research, this stage defines the "what" and "how." Here, user insights and business goals are translated into a concrete blueprint for the product.
Information Architecture (IA) is central to this phase. IA is the practice of organizing, structuring, and labeling content in an effective and sustainable way. Its goal is to help users find information and complete tasks. A solid IA ensures the product is intuitive and scalable.
Key deliverables from this stage include:
- User Personas: Fictional profiles based on research that represent key user segments.
- User Flows: Diagrams illustrating the step-by-step paths users take to complete tasks within the product.
- Sitemaps and Wireframes: Low-fidelity blueprints that outline the structure, content hierarchy, and core functionality of each screen.
Strategic planning is non-negotiable. Building a product without a solid IA is like constructing a building without an architectural plan—it will inevitably be confusing, inefficient, and costly to fix.
Stage 3: Prototyping and Visual Design
With the blueprint established, it's time to bring the product to life visually and interactively. This is where user interface (UI) design takes the lead, transforming static wireframes into tangible, clickable prototypes that simulate the final product experience.
This stage is highly collaborative, with UX and UI designers working together to ensure the visual design is not only aesthetically pleasing but also fully functional and aligned with user-centric principles.
The process typically moves from low to high fidelity:
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes: Basic, clickable wireframes used to test core navigation and user flows.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes: Detailed, pixel-perfect mockups incorporating branding, colors, typography, and interactive elements.
These prototypes are essential for gathering stakeholder and user feedback before committing to code.
Stage 4: Testing and Iteration
The final stage is a continuous cycle of feedback and refinement. Usability testing involves observing real users as they interact with prototypes. This is the moment of truth, where assumptions are validated or disproven by actual human behavior.
The insights gathered from testing are invaluable. They reveal hidden usability issues, points of confusion, and opportunities to enhance the user experience. Based on these findings, the design is refined and re-tested. This iterative loop minimizes risk and ensures the product that launches is polished, validated, and poised for success. We embed this iterative approach into our entire workflow, as detailed in our guide to the 6 steps of the design process.
How to Measure the ROI of UX Design
Strategic user experience delivers measurable financial results. The key to demonstrating this value is tracking the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These metrics bridge the gap between user satisfaction and business success, translating abstract concepts like "usability" into hard data that proves a clear return on investment.
UX measurement is not guesswork. It's about systematically collecting data that reveals how design improvements impact user behavior and sentiment. These metrics can be divided into two main categories: what users do (Behavioral) and what users think (Attitudinal).
Behavioral Metrics: What Users Do
Behavioral metrics are quantitative and focus on observable actions users take within your product. This data is invaluable for proving the direct impact of UX optimizations on business goals. Tools like Google Analytics and Hotjar are essential for tracking these figures.
Key behavioral KPIs include:
- Task Success Rate: The percentage of users who successfully complete a specific goal (e.g., submitting a form, completing a purchase). A low rate is a clear indicator of friction.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of users who take a desired action, such as signing up for a trial or buying a product. Nearly all UX optimization efforts aim to improve this metric. Learn more in our guide to conversion rate optimization best practices.
- Time on Task: The average time it takes a user to complete a task. A lower time typically indicates a more efficient and intuitive design.
- Error Rate: The frequency with which users make mistakes while performing a task. In a fintech app, a high error rate during onboarding can lead to significant user drop-off and increased support costs.
Real-World Example: A B2B SaaS company identified a 35% user error rate on its complex data import feature. After a UX redesign simplified the workflow and added contextual guidance, the error rate fell to just 5%. This not only reduced customer support tickets but also drove higher feature adoption, directly improving customer retention and lifetime value.
Attitudinal Metrics: What Users Think
While behavioral data shows what happened, attitudinal metrics explain why. These metrics capture users' subjective feelings, opinions, and overall satisfaction. This qualitative feedback is critical for understanding the emotional impact of your design and for building lasting brand loyalty.
These metrics are typically gathered through surveys, feedback forms, and user interviews:
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measured with a simple question like, "How satisfied were you with this experience?" on a 1-5 scale, providing a snapshot of user sentiment after a specific interaction.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gauges long-term loyalty by asking, "How likely are you to recommend our product to a friend or colleague?" on a 0-10 scale.
- System Usability Scale (SUS): A standardized 10-question survey that provides a reliable, high-level score for your product's overall usability. A score above 68 is considered above average.
Combining behavioral and attitudinal metrics provides a comprehensive, 360-degree view of your UX performance.
Key UX Metrics and Their Business Impact
| Metric | What It Measures | Business Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Task Success Rate | The percentage of users successfully completing a defined task. | A higher success rate in a checkout flow directly increases sales revenue. |
| Conversion Rate | The percentage of users who perform a desired action. | Improved UX on a signup form can increase qualified leads and grow the sales pipeline. |
| Error Rate | The frequency of user errors while navigating the product. | Reducing errors in a fintech app's transaction process lowers support costs and builds user trust. |
| Customer Satisfaction | Users' reported satisfaction with a product or feature. | High CSAT scores are strongly correlated with higher customer retention and lifetime value. |
| Net Promoter Score | Users' willingness to recommend the product to others. | A high NPS indicates strong brand loyalty and potential for organic growth through word-of-mouth marketing. |
Ultimately, measuring the ROI of UX is about connecting a user-centric design process to the financial health of your business. When you can demonstrate that a streamlined onboarding flow led to a 20% increase in conversions, you are no longer just discussing good design—you are demonstrating smart business strategy.
Real-World UX for Enterprise and Fintech
In high-stakes industries like enterprise software and fintech, effective UX is not a luxury; it is the engine for market adoption, operational efficiency, and a significant competitive advantage. It is how you transform a convoluted process into a simple, guided journey that delivers results.
The UX field has grown exponentially since its beginnings. The cost of poor UX is staggering, with businesses losing an estimated $62 billion annually due to shopping cart abandonment alone. This statistic underscores the critical importance of a user-centered approach. For a deeper look at the profession's evolution, see this article on the 100 years of UX from NNgroup.com.
A Fintech Loan Application Transformed
Consider a regional bank struggling with low completion rates for its online loan application. The digital form was a direct replica of its paper predecessor—a wall of text filled with intimidating financial jargon. User feedback confirmed that customers were confused and abandoning the process midway.
A UX-led redesign focused on simplifying the user's journey:
- Guided Workflow: The single, monolithic form was replaced with a step-by-step wizard that presented questions in small, digestible chunks.
- Progress Indicators: A clear progress bar was added to show users where they were in the process and how much was left.
- Simplified Language: Confusing financial terminology was replaced with plain English, with tooltips providing extra clarity where needed.
The result was a 40% increase in completed loan applications within three months. By focusing on the user's experience, the bank not only boosted a critical business metric but also enhanced its brand reputation for transparency and customer focus.
Enterprise SaaS and Operational Efficiency
In another case, an enterprise SaaS company had a powerful analytics platform that was notoriously difficult to use. New clients required extensive, costly training, and advanced features went largely untouched. The default dashboard was a dense grid of data that overwhelmed non-technical users.
The UX solution was to create role-based dashboards:
- Role-Based Views: Unique dashboards were designed for different user roles—analysts, managers, and executives—each seeing the data most relevant to their responsibilities.
- Data Visualization: Intimidating data tables were replaced with interactive charts and graphs, making it easy to identify trends and insights.
- Contextual Onboarding: Small, targeted tutorials appeared to explain advanced features the first time a user encountered them.
This user-centered overhaul reduced customer training time by 60% and significantly increased the adoption of premium features. By taming complexity, the company lowered its support costs and improved customer retention. These examples demonstrate that strategic UX is an investment that pays for itself many times over. To see more applications in the financial sector, resources from specialists like payments-experts.com are highly valuable.
How to Integrate Expert UX into Your Product Team
Understanding the importance of UX design is the first step. The next, more significant challenge is integrating that expertise into your organization. For many companies, building an in-house UX team is a major obstacle, from the high cost of top-tier talent to the fierce competition for hiring them.
This is where projects often stall. The result is delayed timelines, compromised quality, or UX becoming a last-minute addition. When user experience is not integrated from day one, products are built on assumptions, leading to costly redesigns and missed market opportunities.
A Better Way to Access UX Talent
There is a more direct and predictable path to securing world-class UX expertise. At Group107, we specialize in embedding dedicated, offshore UX/UI experts directly into your product and development teams. This model provides the benefits of an in-house team without the associated overhead and hiring challenges.
Our embedded experts become an integral part of your team. They participate in daily stand-ups, collaborate in real-time with your engineers, and ensure every design decision aligns with your business goals. This seamless integration ensures a user-centric mindset is present from initial concept to final launch.
By bringing in a dedicated expert, you gain a strategic partner invested in your product’s success. This approach transforms UX from a potential bottleneck into a true growth accelerator.
The Business Case for an Embedded UX Expert
The embedded model delivers immediate, measurable advantages that impact your bottom line and accelerate your time-to-market. It is a solution designed for businesses that need to move quickly without sacrificing quality.
Key benefits of this approach include:
- Significant Cost Savings: Access senior-level UX talent at a fraction of the cost of an equivalent in-house hire. Clients often realize up to 60% savings on labor expenses.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Bypass the lengthy hiring process and start building immediately. Our UX designers work in lockstep with your developers, creating an efficient workflow that eliminates delays.
- Seamless Collaboration: Your embedded expert works in your time zone and uses your tools, ensuring clear communication and effective integration with your existing teams.
This model removes the barriers to great UX design, providing the specialized talent needed to build products that capture market share, drive user adoption, and deliver tangible business results. Ready to see how an embedded UX expert can transform your product development? Explore our approach to driving growth with expert teams.
Summary and Next Steps
User experience (UX) design is a critical business function that directly impacts customer loyalty, conversion rates, and profitability. By focusing on creating products that are usable, accessible, desirable, and valuable, you build a sustainable competitive advantage. The process, from research and strategy to prototyping and testing, is a systematic approach to mitigating risk and ensuring your solution truly meets user needs.
Your Actionable Next Steps:
- Audit Your Current UX: Identify one key user journey in your product (e.g., onboarding, checkout). Is it seamless, or are there points of friction? Use behavioral analytics to find where users drop off.
- Gather User Feedback: You don't need a large budget. Conduct five informal usability tests with target users to quickly identify the most significant pain points.
- Prioritize the Biggest Impact: Based on your audit and feedback, identify the single most critical UX issue to fix. Focus your resources on solving that one problem first to achieve a quick, measurable win.
- Evaluate Your Team's Capabilities: Assess whether you have the in-house expertise to execute a user-centric design process effectively. If not, consider a flexible model like an embedded expert to bridge the gap without the overhead of a full-time hire.
At Group107, we embed expert UX designers directly into your team, turning user-centric principles into measurable business results. Let’s build a product your users will love. Learn how we can accelerate your growth at https://group107.com.