A robust quality assurance (QA) process is not an afterthought; it’s a strategic imperative that begins long before the first line of code is tested. It starts with a foundation built on defining what quality means for your business—translating high-level company objectives into clear, measurable standards that drive tangible results. This proactive approach elevates QA from a simple bug-finding exercise to a core driver of business growth and customer satisfaction.
Laying The Foundation For Your QA Strategy
Before writing a single test case, elite QA teams ask a critical question: "What does quality mean for our business?" The answer is never just "a bug-free product."
For a fintech application, quality is defined by flawless transaction security and data integrity. For a global SaaS platform, it’s 99.99% uptime and a frictionless user onboarding experience. This alignment between QA and business outcomes is what transforms quality from a technical checkpoint into a competitive advantage.
In today's fast-paced software landscape, defining these clear, measurable goals has been shown to slash defects by up to 80% in enterprise projects. When you tie QA directly to business outcomes, every testing effort has a purpose and contributes directly to the bottom line. You can explore how this crucial upfront planning fits into the broader development workflow in the software development lifecycle in our detailed guide.
To get a clearer picture of how these stages fit together, here’s a high-level overview of a modern QA process.
The Core Stages Of Quality Assurance
| Stage | Key Objective | Primary Activities | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Strategy & Planning | Define what quality means and how you'll achieve it. | Set business-aligned objectives, define scope, select tools. | Aligns QA efforts with revenue goals and user satisfaction. |
| 2. Test Design | Create a blueprint for how you will test. | Write manual test cases, develop automated test scripts. | Ensures efficient and comprehensive test coverage. |
| 3. Execution | Run tests and identify defects. | Execute test cases, log defects, run regression suites. | Catches issues before they impact customers. |
| 4. Reporting & Metrics | Measure and communicate the state of quality. | Track bug trends, report on test coverage, analyze metrics. | Provides data-driven insights for decision-making. |
| 5. Release & Post-Release | Ensure the product is ready for users and monitor it. | Conduct UAT, monitor production, gather user feedback. | Validates product readiness and captures real-world performance. |
| 6. Continuous Improvement | Learn from data and refine the process. | Hold retrospectives, analyze escapes, update the strategy. | Drives long-term efficiency and product excellence. |
This table illustrates the journey from high-level business goals to ongoing, data-driven refinement—the heartbeat of a truly effective quality assurance program.
Defining Your Quality Objectives
The first critical action in your quality assurance process steps is setting SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound). Vague statements like "improve product quality" are operationally useless. You need tangible, business-focused outcomes.
Here are real-world examples for SaaS and enterprise applications:
- Reduce critical production bugs by 30% within the next quarter to improve system stability.
- Decrease customer support tickets related to software glitches by 20% over six months to lower operational costs.
- Achieve a 95% pass rate for all automated regression tests before each release to accelerate deployment velocity.
- Ensure 100% compliance with WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility standards for all new features to expand market reach.
These objectives provide a clear finish line and form the backbone of your Quality Management Plan (QMP)—the document outlining the standards, practices, and procedures your team will follow. It acts as the single source of truth for your entire QA strategy.
Translating Requirements into Testable Criteria
With objectives set, the next step is to break down business and user requirements into concrete acceptance criteria. This must be a collaborative effort involving product managers, developers, and QA engineers. Every feature requirement needs a clear checklist spelling out its expected behavior from a user's perspective.
For instance, a requirement for a "user login feature" should have acceptance criteria like: "User can log in with a valid email and password," "User sees a specific error message for invalid credentials," and "User is redirected to their personalized dashboard upon successful login."
This level of detail eliminates ambiguity and ensures everyone shares the same vision of what a "done" and "high-quality" feature looks like. You're turning abstract ideas into a practical blueprint for testing, setting the stage for successful execution.
Designing Your Blueprint For Effective Testing
With your objectives defined, it's time to translate that high-level strategy into a detailed operational blueprint. This is where you move from goals to a concrete plan of attack. A well-crafted test plan is your team’s North Star, ensuring every testing effort is deliberate, efficient, and directly tied to business risk.
First, it’s essential to distinguish between a test strategy and a test plan. Your strategy is the "what and why"—the high-level approach and guiding principles. Your test plan is the "who, when, and how"—the granular document detailing specific activities, resources, and timelines. This separation ensures your approach is both strategically sound and tactically executable. For those looking to master this process, a Certified Software Tester Professional course can build the foundational skills needed to architect an effective testing blueprint.
Prioritizing Your Testing Efforts
You cannot test everything with the same level of intensity. The art of a great test plan lies in prioritizing efforts based on business impact and risk. You need a balanced mix of testing methods to achieve comprehensive coverage without wasting cycles on low-priority areas of the application.
A robust testing portfolio should include a smart blend of the following:
- Functional Testing: Verifies that each feature performs its specified function correctly. This is your baseline.
- Performance Testing: Assesses speed, responsiveness, and stability under real-world load conditions.
- Security Testing: Identifies and mitigates vulnerabilities, a non-negotiable for finance, SaaS, and e-commerce platforms.
- Usability Testing: Evaluates how intuitive and user-friendly the application is for a real person.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensures a consistent, high-quality experience across all relevant browsers, devices, and operating systems.
A common mistake is over-investing in functional testing while neglecting performance and security. A risk-based approach forces you to think like a business leader: "What would cause the most damage if it broke?" and allocate your resources accordingly.
Balancing Manual And Automated Testing
One of the most critical decisions in test planning is striking the right balance between manual and automated testing. This isn't an either/or debate; it’s about strategic allocation.
Automation excels at:
- Repetitive, high-volume regression tests.
- Data-driven testing with multiple input variations.
- Performance and load testing simulations.
- API testing.
Manual testing remains essential for:
- Exploratory testing to uncover unexpected defects.
- Usability testing that requires human intuition.
- Complex, one-off scenarios that are impractical to automate.
For a fast-moving enterprise application in a CI/CD pipeline, a robust automation framework isn't a luxury—it's the only way to maintain velocity without sacrificing quality. The ideal mix depends on your project’s maturity, release frequency, and team skillset.
Turning Your Test Plan Into Action
With a solid blueprint in place, it’s time to move from planning to execution. This is where your strategy becomes reality—running tests, identifying defects, and verifying that every feature meets the defined quality standards. This stage is all about disciplined, systematic execution.
Effective test execution demands precision. Every test case, whether manual or automated, must be performed exactly as designed, with results meticulously documented. Simply marking a test as "pass" or "fail" is insufficient. Your team needs detailed logs, screenshots, and environmental data to understand the context behind each outcome. This rigor separates a professional QA process from ad-hoc testing and creates a clear audit trail of your quality efforts.
Managing Defects Efficiently
When a test fails, your defect management workflow is initiated. The goal here is speed and clarity. A vague bug report can waste hours of developer time, creating a bottleneck that stalls the entire release cycle. The objective is to write bug reports so clear that a developer can pinpoint and fix the issue without a lengthy back-and-forth.
A high-quality defect report must include:
- A Clear, Concise Title: Summarize the issue in one sentence (e.g., "User unable to checkout with PayPal on Chrome").
- Steps to Reproduce: Provide an exact, numbered list of actions that trigger the bug. Ambiguity is the enemy of efficiency.
- Expected vs. Actual Results: State what should have happened versus what actually occurred.
- Supporting Evidence: Attach screenshots, video recordings, or console logs to provide visual proof and technical context.
- Environment Details: Specify the browser, OS, device, and application version used during testing.
The ultimate goal is to remove all guesswork. A developer should be able to replicate the bug on their first attempt, which dramatically reduces the Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR). Tools like Jira and Azure DevOps are indispensable for managing this lifecycle, tracking each defect from discovery to resolution.
The Critical Role of Regression Testing
Once a defect is fixed, the work isn't done. This is where regression testing becomes absolutely critical. Its purpose is to ensure that the new fix hasn't inadvertently broken existing functionality—a surprisingly common side effect in complex software.
In any modern development environment, automated regression suites are the backbone of this process. Manually running thousands of checks before every release is not feasible. To learn more about building a solid testing framework, explore our guide on software testing best practices. By automating regression tests, your team can deploy changes with confidence, knowing they haven't introduced new problems while solving old ones.
Integrating QA Into Your DevOps Pipeline
In today's high-velocity development landscape, the notion that you must choose between speed and quality is obsolete. The real innovation lies in weaving your quality assurance process steps directly into the fabric of your CI/CD pipeline. This is the essence of "shifting left"—transforming QA from a final gate into a continuous, early-stage activity.
By automating crucial tests—such as smoke, integration, and end-to-end tests—to trigger with every code commit, you create a powerful, immediate feedback loop. Developers are notified of bugs in minutes, not days, allowing them to fix issues while the code is still fresh in their minds. This dramatically reduces the cost and complexity of remediation.
Fostering a Culture of Shared Quality
This is more than a workflow adjustment; it's a fundamental cultural shift that dismantles the traditional silos between development, QA, and operations. You are building a true DevOps environment where quality is everyone's responsibility.
In this model, developers are the first line of defense, writing unit and integration tests for their code. QA engineers evolve from manual testers into quality advocates, designing robust automation frameworks, performing deep risk analysis, and enabling the entire team to build quality in from the start.
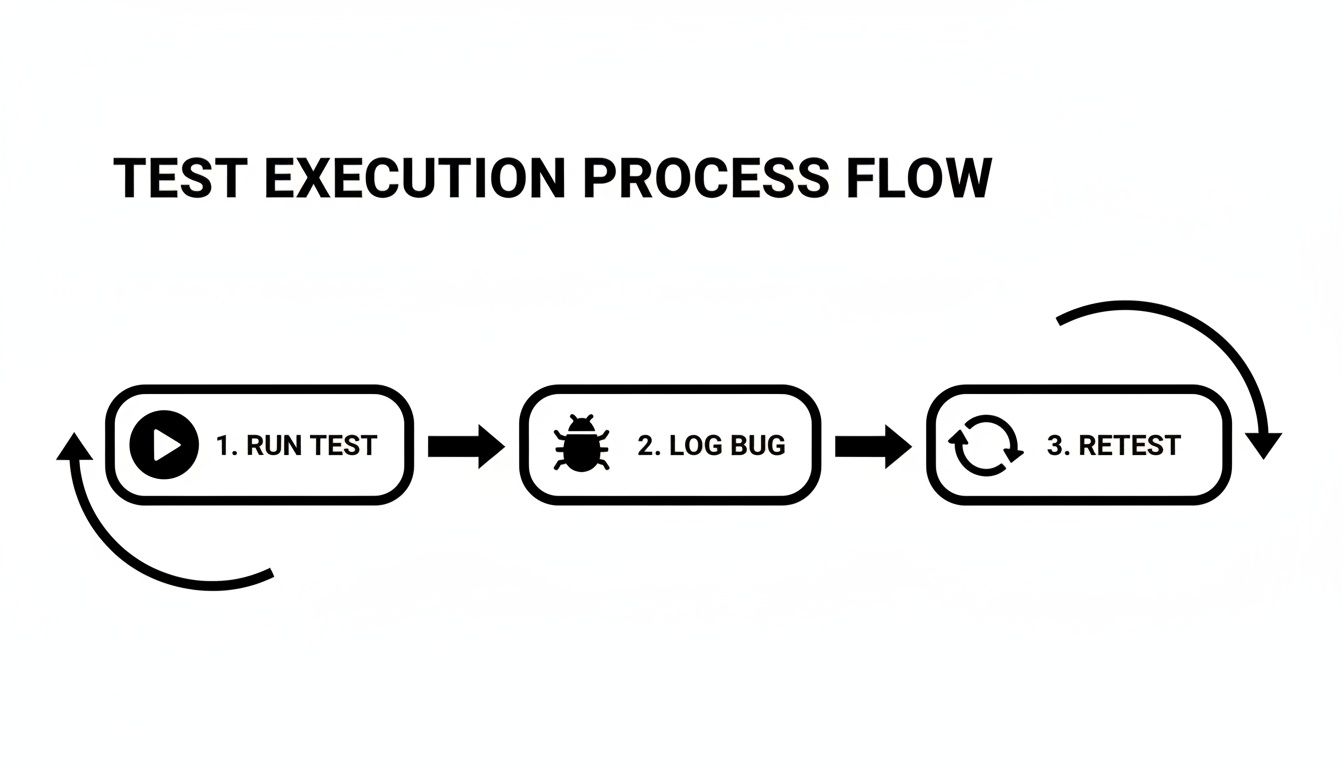
This diagram illustrates this tight, iterative cycle in practice.
As you can see, tests run constantly. When a bug is found, it's logged and retested in a rapid loop, preventing defects from ever reaching the main codebase.
For any organization aiming to ship faster without compromising stability, this integrated approach is the only way forward. To make this work, you need solid strategies for implementing Agile DevOps.
Key Automation Stages in the Pipeline
Embedding QA means strategically placing automated checkpoints throughout your pipeline to validate code as it progresses toward production.
A typical breakdown includes:
- Commit Stage: Static code analysis and unit tests run automatically upon code commit. This is the fastest, first-pass check for syntax errors and basic logic flaws.
- Build Stage: After a successful build, a more extensive set of integration tests run to ensure the new code works harmoniously with existing modules.
- Test Stage: The build is deployed to a staging environment where automated smoke tests, API tests, and critical end-to-end user journeys are executed.
By the time a feature reaches a human for exploratory or user acceptance testing (UAT), it has already passed multiple layers of automated validation. This dramatically increases the team's confidence in the release candidate.
A well-architected pipeline ensures quality is an ingredient, not a garnish. To dive deeper into the mechanics, it's worth exploring what a CI/CD pipeline is and why it's crucial. This is the engine that drives modern, high-velocity software delivery.
Measuring QA Performance And Driving Improvement
A world-class QA process is not a "set it and forget it" system. It is a living, evolving part of your organization that requires continuous data-driven refinement. When you measure the right key performance indicators (KPIs), you can shift the perception of QA from a "cost center" to a strategic partner that drives business value. This is about more than counting bugs; it's about demonstrating the tangible impact of quality on the development lifecycle and, ultimately, your customers.
Key QA Metrics That Actually Matter
Avoid drowning in vanity metrics. Instead, focus on a handful of KPIs that provide a clear, actionable picture of your QA process's health and business impact.
- Defect Escape Rate (DER): This is the ultimate measure of QA effectiveness. DER tracks the percentage of defects that slip past your internal processes and are found in production by users. A high DER is a critical signal that your test coverage or strategy needs immediate attention.
- Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): This metric measures the average time from when a defect is reported to when the fix is verified. A low MTTR indicates strong collaboration between development and QA teams and an efficient workflow.
- Test Coverage: This quantifies what percentage of your codebase is covered by tests (both automated and manual). It helps identify blind spots and areas of high risk in your application.
- Automated Test Pass Rate: In a CI/CD pipeline, the stability of your automation suite is paramount. A consistently low pass rate can indicate flaky tests that need refactoring or systemic issues in new code builds.
By tracking these metrics, you can build dashboards that tell a compelling story to stakeholders. Visualizing trends in DER or MTTR provides a powerful, data-backed narrative about the ROI of your quality initiatives.
Establishing A Continuous Improvement Loop
Measuring performance is only half the battle. The real value is realized when you use that data to create a powerful feedback loop. This cycle is what separates good QA teams from great ones.
It begins with post-release monitoring to see how your product performs in the wild. This raw, unfiltered data from users and performance logs is invaluable. This is the final, crucial step: feeding what you learn from metrics like defect escape rates right back into the system to make it better.
For instance, CGIAR's process, which famously achieved an 80%+ comment acceptance rate, is a perfect example of how sustained refinement leads to incredible outcomes. You can discover more about their successful quality assurance process.
By analyzing real-world data alongside your internal QA metrics, you can spot patterns. Are users struggling with a new feature? Are performance issues emerging under real-world load? These insights must be fed directly back into your planning for the next sprint. This proactive approach transforms your QA process from a simple gatekeeper into a strategic engine for continuous product improvement.
Summary and Next Steps
Mastering the quality assurance process steps is essential for any business that wants to deliver high-quality digital products efficiently and consistently. By moving beyond simple bug hunting to a strategic, data-driven approach, you can reduce costs, accelerate delivery, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways:
- Start with Strategy: Align your QA objectives directly with your business goals to ensure every testing effort delivers value.
- Plan Methodically: Create a detailed test plan that prioritizes efforts based on risk and strategically balances manual and automated testing.
- Execute with Precision: Implement a rigorous process for test execution and defect management to ensure clarity and speed.
- Integrate and Automate: Weave QA into your CI/CD pipeline to create a culture of shared quality and enable rapid, confident releases.
- Measure and Improve: Use meaningful metrics like Defect Escape Rate and MTTR to continuously refine your process and demonstrate ROI.
Actionable Next Step:
Review your current QA process. Are your objectives tied to business outcomes? Are you measuring the right KPIs to drive improvement? Start by identifying one stage of your process—from planning to post-release monitoring—and implement one data-driven change to enhance its effectiveness this quarter.
At Group 107, we build and manage dedicated offshore teams that embed these quality principles into every stage of your development lifecycle, ensuring your digital products are not only built fast but built right. Discover how we can help you scale with confidence at https://group107.com.